The Ultimate Cosmos Guide
Cosmos is an ecosystem of independent blockchains that can scale and communicate with each other
In this thread, we will cover:
Logic behind why Cosmos was created
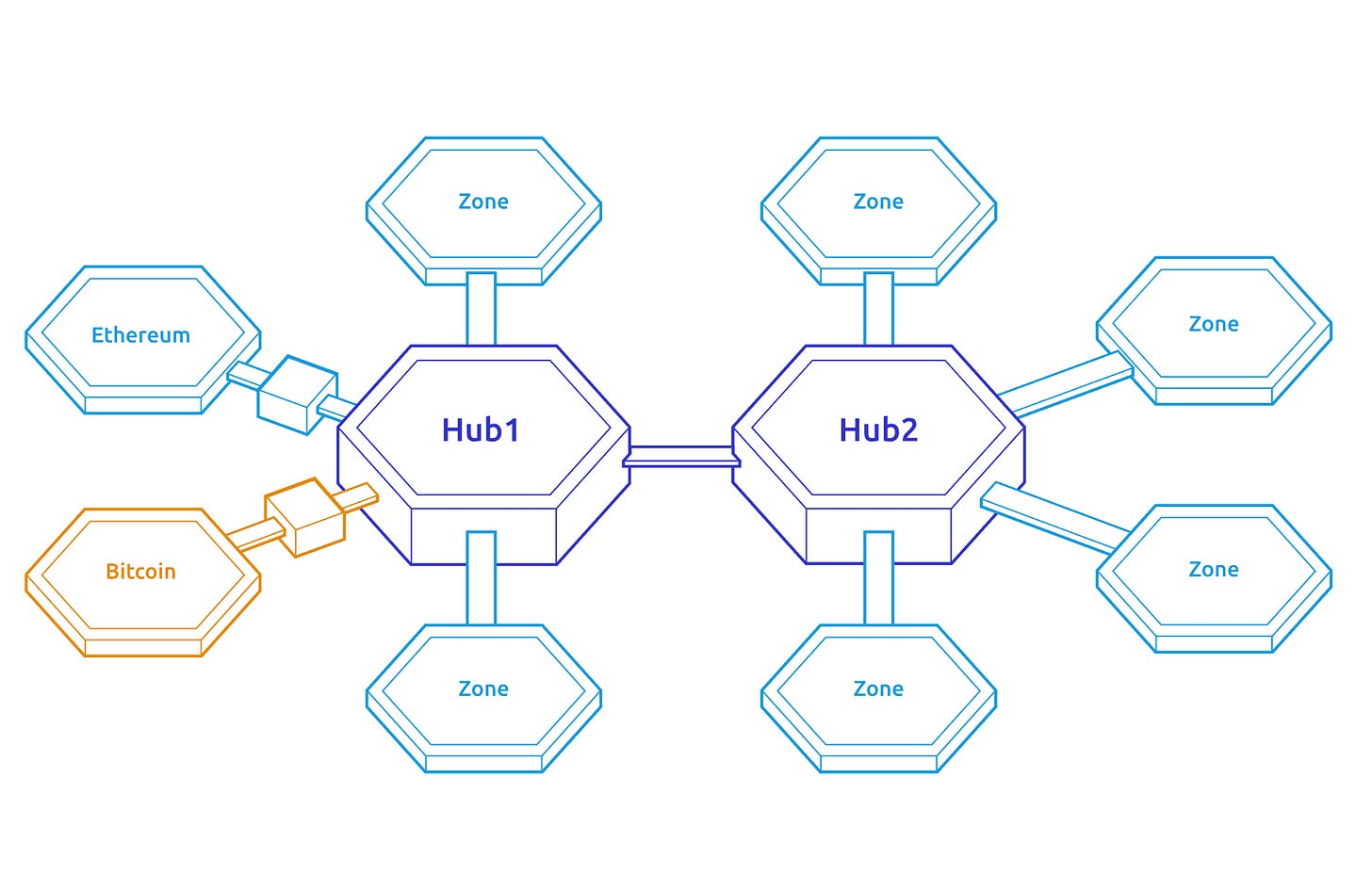
Hubs & Zones
Tendermint
IBC
Cosmos SDK
Interchain Security
Thoughts on $ATOM tokenomics
Concerns
Interesting projects building on Cosmos
Developments
Why Cosmos was created
PoW chains aren't sustainable in the long run
Blockchains are slow and siloed
dApps have many existing problems
Creating a chain is hard, it takes lots of time and resources
Cosmos was created to solve all of these problems.
What is Cosmos?
Cosmos is an ecosystem of independent blockchains that can scale and communicate with each other. Cosmos is not a blockchain — it is a blueprint for designing application-specific blockchains, called Zones.
The Cosmos ecosystem consists of Hubs and Zones. Creating Hubs and Zones is permissionless.
Hubs
The Hub on the Cosmos network is the first blockchain. It acts as a router for Zones. $ATOM is the utility token of the Cosmos Hub. Cosmos Hub is designed to be minimalistic, it doesn't support smart contracts.
As of now, there are 2 Hubs on the Cosmos network:
Cosmos Hub
IRIS Hub
Why is the Hub the way it is?
It doesn't support smart contracts because introducing smart contracts also introduces risk of exploit. The Hub is designed to create an interoperable & scalable economy by allowing thousands of Zones to be connected with each other.
Functions of the Hub
Connect with many Zones through IBC
Enable data packets to transfer to these Zones
Keep track of the total # of tokens on each side chain
The Hub doesn't care about the logic or state of the connected Zones, which can be related to anything (e.g. gaming, content, payments). All it knows is who is responsible for signing & how the validator set is mutating.
What are Zones?
Zones are Blockchains that are connected to the Hub. Zones have their own tokens & validator sets. And as of now, there are currently 49 Zones in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Each Zone is powered by consensus algorithms that have fast finality like Tendermint. This means that any Blockchain with fast finality can be connected to the Hub and use IBC.
PoW blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin can also be connected to the Hub. More on that here.
What is Tendermint?
Tendermint is a consensus engine, but also an algorithm. An analogy to explain Tendermint: Cosmos is like a worldwide web of computers running on various operating systems. In this analogy, Tendermint is an operating system – like Windows or Linux.
It's also a solution that packages the Consensus & Networking layers of blockchain into a generic engine. This allows developers to focus only on application layer development rather than the complex generic engine. This alone saves years in development time.
The TBFT engine is connected to the application layer by ABCI (Application Blockchain Interface). This layer can be wrapped in any programming language, making it possible for developers to choose a language that fits their needs.
What is Cosmos SDK?
Cosmos SDK is a development framework that helps in Blockchain creation for any use case. It is modular, so devs can tweak various parts of the Blockchain to suit their needs. This modularity is the main reason why many dApps are building on Cosmos.
Cosmos SDK comes with some pre-baked modules like the IBC module, staking, governance fee distribution, and banking module to help with the multi-assets. Developers can use these, so they don't have to build everything from scratch.
Here are some popular protocols built using Cosmos SDK:
How does Cosmos take interoperability to the next level?
The connection between Blockchains is achieved by Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC). IBC is more than just a bridge, it's a general-purpose message-passing protocol.
Let's understand IBC through an analogy: IBC is like a mail delivery system. When you send a package to someone, you send it through a postal service that collects the package and deposits it into the recipient's mailbox.
The postal service doesn't care about the contents inside the parcel. It doesn't matter what's in the parcel. Same with IBC - it can pass along any message.
How does IBC work?
IBC leverages the instant finality of Tendermint, although it can also work with any fast-finality blockchains. IBC is like TCP/IP.
IBC utilizes Light Client for the bridge. This means that if you trust two particular chains then there is no additional trust assumption required. Here's a fantastic thread by @Thyborg_ on IBC security:

Interchain Security
Interchain security allows for a parent chain (like Cosmos Hub), to be in charge of producing blocks for a consumer chain.
Why Interchain Security?
In order to secure PoS chains, they must be secured by a decentralized validator set, with a valuable staking token. This means the chain’s security is directly tied to the market cap of the staking token.
With Interchain Security, the consumer chain will be secured by the validator set of the Cosmos Hub (directly related to the $ATOM market cap).
How does it work?
It does this by sharing the set of parent chain validators who are in charge of producing blocks. The participating validators would run two nodes:
One for the Cosmos Hub
One for the consumer chain and receive fees and rewards on both chains
Tokenomics of $ATOM
ATOM is inflationary (currently at 12%) per annum which makes it less attractive for speculators. Although it can be used to pay transaction fees and staking on the Cosmos Hub, that isn't the main intent.
Let's understand $ATOM through an analogy in the words of @jaekwon. $ATOM can be thought of as an ASIC miner for Bitcoin. Everyone can use the Bitcoin blockchain. But not everyone wants to mine Bitcoin or have an ASIC miner.
With the introduction of Interchain Security, the ASIC miner, which was used to mine $BTC, can now be used to mine every other PoW chain. Users will be able to use $ATOM to secure the Cosmos Hub as well as consumer chains. This means that they will earn rewards in $ATOM and in the native token of the consumer chain.
Conclusion
For now, $ATOM accrues value from staking rewards & airdrops. If you count only the Airdrops $ATOM stakers have received, that alone has been worth thousands of dollars. But with interchain security, the value accrual mechanism of $ATOM grows exponentially.
Concerns
Cosmos eco still doesn't have any native stablecoin support as of now
Few protocols have launched their mainnet without any native stablecoin support
Some protocols are too reliant on bridges
Some interesting projects building on Cosmos
@_gnoland: Concurrent Smart Contracts that scale by utilizing gnolang (fork of Golang)
@agoric: L1 where developers can deploy smart contracts in Javascript
@dYdX: Decentralized perpetual exchange moving from Starkware
@TeamKujira: L1 platform for community-selected projects creating true value
Developments
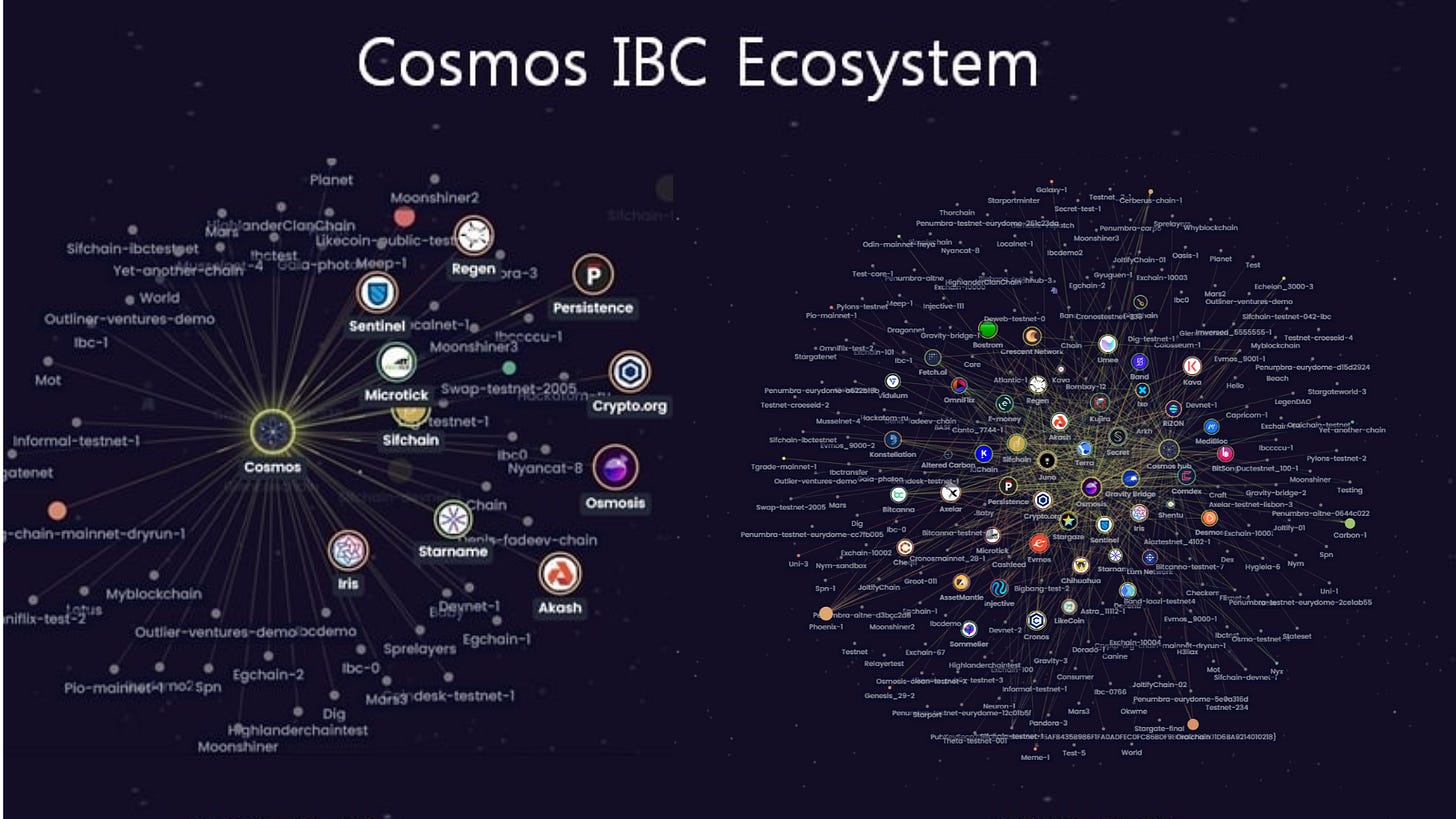
So far the Cosmos ecosystem is growing exponentially, and it seems likely that it will continue to do so. Here's a picture of the Cosmos ecosystem 2 years apart:
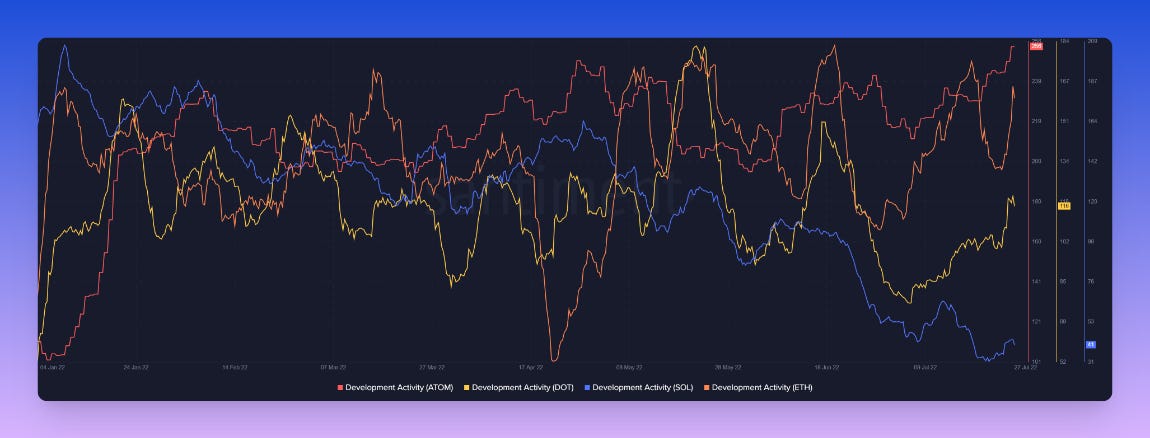
Development activity on Cosmos is higher in 2022 compared to Solana, Ethereum, and Polkadot.
Here are some Cosmos chads and devs to follow:
Some awesome additional resources
@jaekwon interview:
Cosmos & IBC:
https://research.paradigm.xyz/cosmos-thesis
https://v1.cosmos.network/intro
Interchain Security:
https://blog.cosmos.network/interchain-security-is-coming-to-the-cosmos-hub-f144c45fb035
Subscribe to receive our weekly newsletter and in-house research content!
Please Share, Leave Feedback, and Follow Us on Twitter, Telegram, and LinkedIn to stay connected with us.